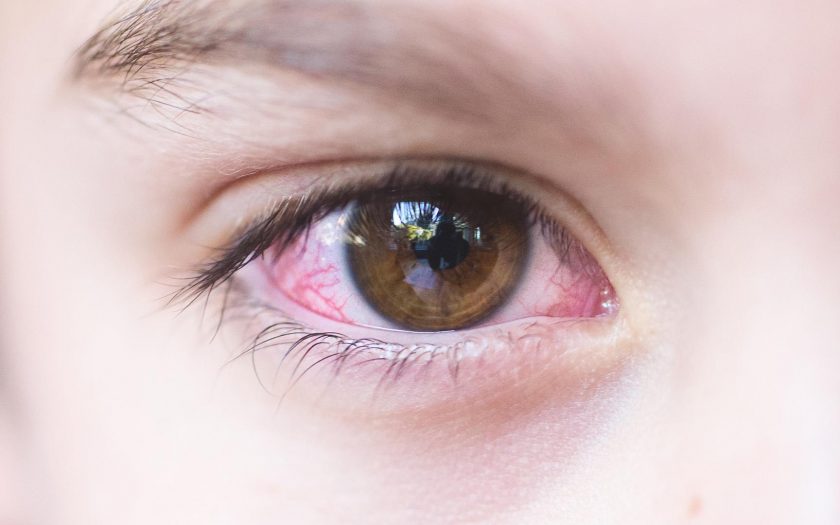
Allergic conjunctivitis is a reactive pathology of the conjunctiva caused by immune reactions in response to contact with the allergen. Allergic conjunctivitis manifests by hyperemia and swelling of the mucous membrane of the eye, itching, and swelling of the eyelids, tears, and photophobia. In the treatment of allergic conjunctivitis, antihistamines, topical corticosteroids, and specific immunotherapy are used.
Causes
Common in the etiology of all forms of allergic conjunctivitis is the increased sensitivity to various environmental factors. Due to the features of anatomical structure and location, the eyes are most prone organs to contact with exogenous allergens.
Depending on the etiology, distinguish:
- Seasonal allergic conjunctivitis. Pollen conjunctivitis (hay fever, pollen allergy) caused by pollen allergens during the flowering of herbs, trees, cereals. Aggravation of pollen conjunctivitis associated with the period of flowering of plants in one region or another. Seasonal allergic conjunctivitis in 7% of patients is exacerbated in the spring (at the end of April to the end of May), 75% in summer (in the beginning of June to late July), 6.3% in the offseason (in late July to mid-September) , which, correspondingly, coincides with the pollination of trees, meadow grasses and weeds.
- Spring conjunctivitis. The etiology of spring conjunctivitis has been studied little. The disease is aggravated in the spring – at the beginning of summer and regressed in the fall. This form of allergic conjunctivitis usually passes involuntarily during puberty, which suggests a certain role of the endocrine factor in its development.
- Chronic allergic conjunctivitis. It is more than 23% of all allergic eye diseases. Direct allergens, in this case, are usually home dust, animal hair, dry fish food, feathers, down, food products, perfumes, cosmetics, and household chemicals. Chronic allergic conjunctivitis is often associated with eczema and bronchial asthma.
Symptoms of allergic conjunctivitis
Allergies are usually affecting both eyes. Symptoms develop from a few minutes to 1-2 days from the time of exposure to the allergen. Allergic conjunctivitis is characterized by strong itching of the eyes, edema of the conjunctiva; in the severe course – the development of photophobia, blepharospasm, and ptosis.
In some forms of allergic conjunctivitis (spring and atopic keratoconjunctivitis) there is a corneal lesion. At a medical allergy, lesions of the cornea, retina, skin of eyelids, the optic nerve can be observed. Acute drug conjunctivitis sometimes manifests by anaphylactic shock and acute urticaria.
In chronic allergic conjunctivitis, the symptoms are poorly expressed. Typical complaints are periodic itching of the eyelids, burning eyes, redness of the eyelids and tear.
Treatment of allergic conjunctivitis
With allergic conjunctivitis used antihistamines, anti-allergic eye drops (levocabastin, azelastin, olopatadine). At a lesion of a cornea used eye drops with dexpanthenol and vitamins.
Severe forms of allergic conjunctivitis may require the appointment of topical corticosteroids (Loteflam Eye Drops, Pred Forte Eye Drops), topical NSAIDs (eye drops with diclofenac). Recurrent allergic conjunctivitis can be treated by specific immunotherapy.